Federated Learning with Dynamic Epoch Adjustment and Collaborative Training in Mobile Edge Computing
 Xiangyi Chen
Xiangyi Chen
Abstract
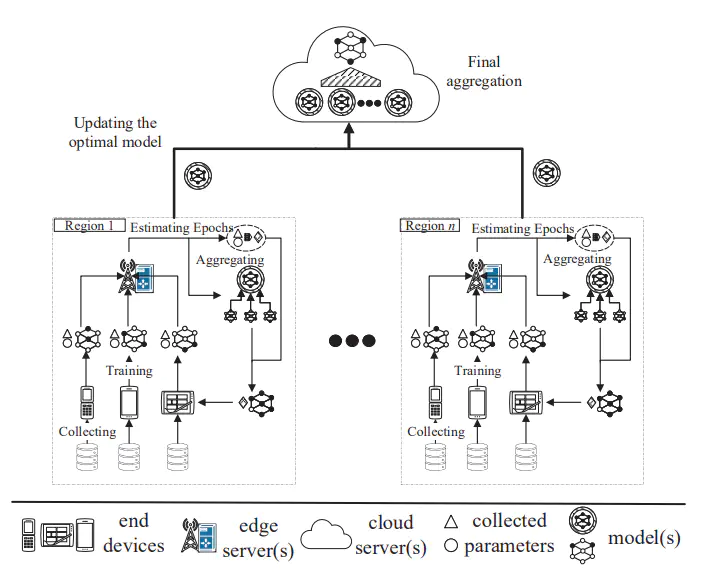
As a distributed learning paradigm, federated learning (FL) can be applied in mobile edge computing (MEC) to support real-time artificial intelligence by leveraging edge computation resources while preserving data privacy in the end devices. However, the unpredictable wireless connections between end devices and edge servers in MEC (e.g., frequent handovers and unstable wireless channels) may result in the loss of important model parameters, which slows down the FL training process and degrades the quality of the global model. In this paper, we propose an adaptive collaborative federated learning (ACFL) scheme to accelerate the convergence and improve model reliability by mitigating communication-based parameter loss under a three-layer MEC architecture. Firstly, a dynamic epoch adjustment method is proposed to reduce communication rounds by dynamically adjusting the training epochs in end devices. In addition, to accelerate the FL convergence, we present an edge server collaborative training scheme by leveraging a multi-layer computing architecture, where edge servers utilize their maintained data to collaboratively train models with end devices. Finally, extensive simulations are conducted and show that ACFL can efficiently improve model reliability and accelerate the convergence of the FL process in MEC.